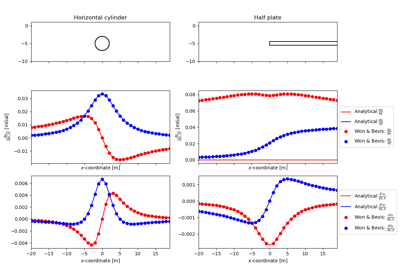
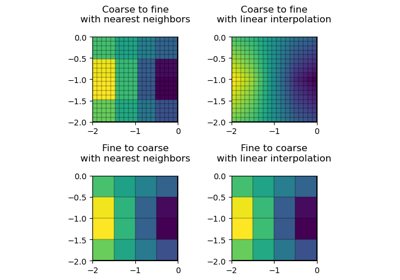
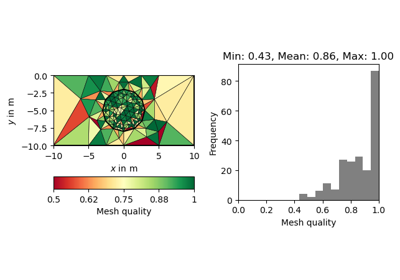
#!/usr/bin/env python
# -*- coding: utf-8 -*-
"""
Created on Tue Jul 07 09:44:36 2015
@author: Marcus
"""
import heapq
import pygimli as pg
import numpy as np
from pygimli.physics.traveltime.ratools import createGradientModel2D
def findSlowness(edge):
"""Retrieve fastest cell neighboring an edge."""
assert hasattr(edge, 'leftCell') and hasattr(edge, 'rightCell')
if edge.leftCell() is None:
slowness = edge.rightCell().attribute()
elif edge.rightCell() is None:
slowness = edge.leftCell().attribute()
else:
slowness = min(edge.leftCell().attribute(),
edge.rightCell().attribute())
return slowness
[docs]def fastMarch(mesh, downwind, times, upT, downT):
"""Do one front marching."""
upCandidate = []
for node in downwind:
neighNodes = pg.commonNodes(node.cellSet())
upNodes = []
for n in neighNodes:
if upT[n.id()]:
upNodes.append(n)
if len(upNodes) == 1: # the Dijkstra case
edge = pg.findBoundary(upNodes[0], node)
if edge is None:
continue
raise StandardError("no edge found")
tt = times[upNodes[0].id()] + \
findSlowness(edge) * edge.shape().domainSize()
# use node id additionally in case of equal travel times
heapq.heappush(upCandidate, (tt, node.id(), node))
else:
cells = node.cellSet()
for c in cells:
for i in range(c.nodeCount()):
edge = pg.findBoundary(c.node(i), c.node((i + 1) % c.nodeCount()))
a = edge.node(0)
b = edge.node(1)
ta = times[a.id()]
tb = times[b.id()]
if upT[a.id()] and upT[b.id()]:
line = pg.Line(a.pos(), b.pos())
t = min(1., max(0., line.nearest(node.pos())))
ea = pg.findBoundary(a, node)
eb = pg.findBoundary(b, node)
#if ea is None or eb is None:
#print(a, b, node)
if t == 0:
slowness = findSlowness(ea)
elif t == 1:
slowness = findSlowness(eb)
else:
slowness = c.attribute()
ttimeA = (ta + slowness * a.pos().distance(node.pos()))
ttimeQ = (ta + t * (tb - ta)) + \
slowness * line(t).distance(node.pos())
ttimeB = (tb + slowness * b.pos().distance(node.pos()))
tmin = min(ttimeA, ttimeQ, ttimeB)
heapq.heappush(upCandidate, (tmin, node.id(), node))
candidate = heapq.heappop(upCandidate)
newUpNode = candidate[2] # original
times[newUpNode.id()] = candidate[0]
upT[newUpNode.id()] = 1
downwind.remove(newUpNode)
newDownNodes = pg.commonNodes(newUpNode.cellSet())
# newUpNodeId = candidate[1] # original
# times[newUpNodeId] = candidate[0]
# upT[newUpNodeId] = 1
# downwind.remove(newUpNodeId)
# newDownNodes = pg.commonNodes(mesh.node(newUpNodeId).cellSet())
for nn in newDownNodes:
if not upT[nn.id()] and not downT[nn.id()]:
downwind.add(nn)
downT[nn.id()] = 1
class TravelTimeFMM(pg.ModellingBase):
"""Modelling class using the Fast Marching Method (FMM).
It can be used alternatively to Dijkstra modelling.
However, currently it is quite slow.
A implementation in C++ might speed up.
"""
dataMatrix = np.zeros((0, 0))
timeMatrix = np.zeros((0, 0))
def __init__(self, mesh=None, data=None, frequency=200,
verbose=False, debug=False):
"""
Init function.
Parameters
----------
mesh : pygimli.Mesh
2D mesh to be used in the forward calculations.
data : pygimli.DataContainer
The datacontainer with sensor positions etc.
frequency : float [200]
middle frequency for computing thickness of fat ray
verbose : boolean
More printouts or not...
"""
pg.ModellingBase.__init__(self, verbose)
super(TravelTimeFMM, self).__init__(verbose=verbose)
self.debug = debug
self.frequency = frequency
if data is None:
self.setData(pg.DataContainer())
elif isinstance(data, str):
self.data_ = pg.DataContainer(data, "s g")
self.setData(self.data_)
else:
self.setData(data)
if mesh is not None:
mesh.createNeighbourInfos() # generates leftCell/rightCell
self.setMesh(mesh) # besser use createRefinedForwardMesh
def setMesh(self, mesh):
"""Set mesh"""
super(TravelTimeFMM, self).setMesh(mesh)
self.prepareMatrices()
def setData(self, data):
"""Set data and prepare stuff"""
super(TravelTimeFMM, self).setData(data)
self.prepareMatrices()
def prepareMatrices(self):
"""Prepare some matrices being filled by response and Jacobian."""
if (isinstance(self.mesh(), pg.Mesh) and
isinstance(self.data(), pg.DataContainer)):
nSensors = self.data().sensorCount()
nModel = self.mesh().cellCount()
self.dataMatrix = np.zeros((nSensors, nSensors))
self.timeMatrix = np.zeros((nSensors, nModel))
if self.debug:
print("shapes:", self.dataMatrix.shape, self.timeMatrix.shape)
def computeTravelTimes(self, slowness, calcOthers=False):
"""Compute the travel times and fill data and time matrix
for later use of response and Jacobian, respectively.
For response only active sources are needed, for Jacobian all.
"""
mesh = self.mesh()
nNodes = mesh.nodeCount()
midPoints = self.mesh().cellCenters()
param_markers = np.unique(mesh.cellMarkers())
param_count = len(param_markers)
data = self.data()
if len(slowness) == mesh.cellCount():
mesh.setCellAttributes(slowness)
# self.mapModel(slowness)
elif len(slowness) == param_count:
# map the regions in the mesh to slowness
slow_map = pg.stdMapF_F()
min_reg_num = min(param_markers)
for i, si in enumerate(slowness):
slow_map.insert(float(i+min_reg_num), si)
mesh.mapCellAttributes(slow_map)
else:
raise ValueError("Wrong no of parameters. Mesh size: {}, no "
"of regions: {}, and number of slowness values:"
"{}".format(mesh.cellCount(), param_count,
len(slowness)))
times = pg.RVector(nNodes, 0.)
upTags = np.zeros(nNodes)
downTags = np.zeros(nNodes)
sourceIndices = np.unique(data("s"))
if calcOthers:
ns = len(sourceIndices)
geophoneIndices = np.setxor1d(np.arange(data.sensorCount()),
sourceIndices)
sourceIndices = geophoneIndices
# geophoneIndices = np.unique(data("g"))
if self.debug:
print("{:d}-{:d}={:d}".format(
data.sensorCount(), ns, len(sourceIndices)))
# if self.debug: # resize not working
# self.solution().resize(self.mesh().nodeCount(), self.nSensors)
# print(self.solution().rows(), self.solution().cols())
for iSource in np.array(sourceIndices, dtype=int):
if self.debug:
print(iSource)
# initial condition (reset vectors)
times *= 0.0
upTags *= 0
downTags *= 0
downwind = set()
source = data.sensorPosition(int(iSource))
cell = mesh.findCell(source)
# fill in nodes around source using local smoothness
for i, n in enumerate(cell.nodes()):
times[n.id()] = cell.attribute() * n.pos().distance(source)
upTags[n.id()] = 1
for i, n in enumerate(cell.nodes()):
tmpNodes = pg.commonNodes(n.cellSet())
for nn in tmpNodes:
if not upTags[nn.id()] and not downTags[nn.id()]:
downwind.add(nn)
downTags[nn.id()] = 1
while len(downwind) > 0: # start fast marching
fastMarch(mesh, downwind, times, upTags, downTags)
self.dataMatrix[iSource] = pg.interpolate(
mesh, times, destPos=data.sensorPositions())
self.timeMatrix[iSource] = pg.interpolate(
mesh, times, destPos=midPoints)
if self.debug:
print(self.solution().rows(), self.solution().cols())
print(len(times), self.mesh())
self.solution()[int(iSource)] = times
self.solution().setCol(int(iSource), times)
def response(self, slowness):
"""
Response function. Returns the result of the forward calculation.
Uses the shot- and sensor positions specified in the data container.
"""
self.computeTravelTimes(slowness)
# assembling the data from the data matrix
data = self.data()
t_fmm = pg.RVector(data.size())
for i in range(data.size()):
t_fmm[i] = self.dataMatrix[int(data("s")[i])][int(data("g")[i])]
return t_fmm
def createJacobian(self, slowness):
"""Jacobian matrix using a fat-ray approach (Jordi et al. 2016)."""
data = self.data()
self.jacobian().resize(data.size(), self.mesh().cellCount())
# first compute reciprocal travel times for geophone sources
self.computeTravelTimes(slowness, calcOthers=True)
n_data = data.size()
cellSizes = self.mesh().cellSizes()
for i in range(n_data):
iS, iG = int(data("s")[i]), int(data("g")[i])
tsr = self.dataMatrix[iS][iG] # shot-receiver travel time
dt = self.timeMatrix[iS] + self.timeMatrix[iG] - tsr # difference
weight = np.maximum(1 - 2 * self.frequency * dt, 0.0) # 1 on ray
if self.debug:
print(pg.sum(pg.sign(weight)))
wa = weight * cellSizes
if np.sum(wa) > 0: # only if all values are zero
wa /= np.sum(wa)
self.jacobian()[i] = wa * tsr / slowness
# self.jacobian()[i] = wa / np.sum(wa) * tsr / slowness
# TODO: check "invalid value in true divide" warning
def createDefaultStartModel(self):
"""Create a meaningful starting model in case none is given."""
return pg.RVector(self.fop.regionManager().parameterCount(), 0.001)
if __name__ == '__main__':
# Set up FMM modelling operator and run a synthetic model
mydata = pg.DataContainer('example_topo.sgt', 's g')
print(mydata)
mymesh = pg.meshtools.createParaMesh(mydata, boundary=0, paraBoundary=5,
paraDepth=20,
quality=34.5, paraMaxCellSize=5)
mymesh.createNeighbourInfos()
print(mymesh)
slo = createGradientModel2D(mydata, mymesh, vTop=1000, vBot=2000)
fwd = TravelTimeFMM(mymesh, mydata, frequency=500) #
fwd.createRefinedForwardMesh(False)
resp = fwd.response(slo)
mydata.set('t', resp)
print("ready with response, starting jacobian")
fwd.createJacobian(slo)
raise SystemExit
# %%
pg.plt.imshow(fwd.dataMatrix, interpolation='nearest')
# %%
one = pg.RVector(mydata.size(), 1.0)
coverage = fwd.jacobian().transMult(one)
pg.show(fwd.mesh(), coverage/fwd.mesh().cellSizes())